Coaxial wet-spun yarn supercapacitors for high-energy density and safe wearable electronics |
| Time£º2014-05-19 13:01 |
Liang Kou, Tieqi Huang, Bingna Zheng, Yi Han, Xiaoli Zhao, Karthikeyan Gopalsamy, Haiyan Sun and Chao Gao. Nature Communications, 5, Article number: 3754.
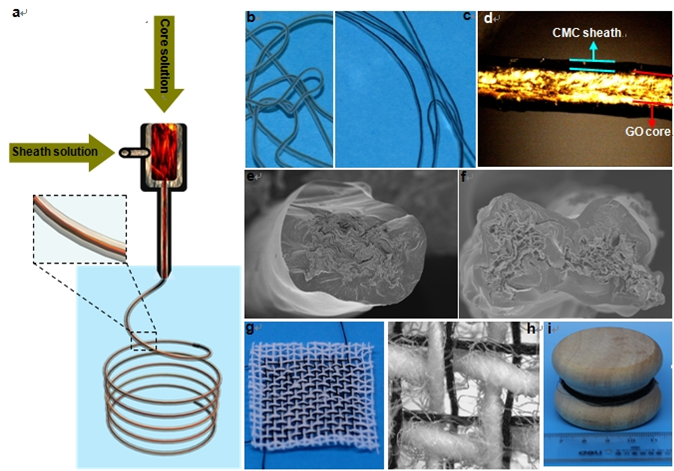
Abstract: Yarn supercapacitors have great potential in future portable and wearable electronics because of their tiny volume, flexibility and weavability. However, low-energy density limits their development in the area of wearable high-energy density devices. How to enhance their energy densities while retaining their high-power densities is a critical challenge for yarn supercapacitor development. Here we propose a coaxial wet-spinning assembly approach to continuously spin polyelectrolyte-wrapped graphene/carbon nanotube core-sheath fibres, which are used directly as safe electrodes to assembly two-ply yarn supercapacitors. The yarn supercapacitors using liquid and solid electrolytes show ultra-high capacitances of 269 and 177 mF cm−2 and energy densities of 5.91 and 3.84 μWh cm−2, respectively. A cloth supercapacitor superior to commercial capacitor is further interwoven from two individual 40-cm-long coaxial fibres. The combination of scalable coaxial wet-spinning technology and excellent performance of yarn supercapacitors paves the way to wearable and safe electronics.
 |
Read£º5267
|
