News
| Immobilization of Enzymes on 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate and Glycidyl Methacrylate Copolymer Brushes |
| Time:2014-07-10 14:00 Source:未知 Author:polymer Click: |
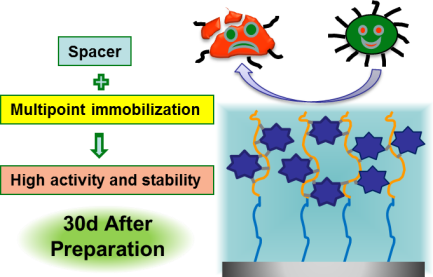
The immobilization of enzymes is of paramount importance to maintain their activity and stability. In this study, surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization was applied to prepare poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-b-poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-glycidyl methacrylate) brushes on glass slides. The polymerization kinetics was followed by quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation and ellipsometry in terms of mass and thickness growth, respectively. The surface chemical compositions of the obtained polymer brushes were characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Their mass, thickness and enzyme immobilization ability could be easily tuned by the initiator reaction time, monomer ratio and polymerization time. The anti-bacteria activity and stability of the immobilized lysozymes were studied by fluorescent staining and bacteria lysis assay, revealing that the lysozymes on the copolymer brushes had good stability against storage at 4oC for up to 30 days.
Tanchen Ren, Zhengwei Mao*, Sergio Enrique Moya, Changyou Gao*, Immobilization of enzymes on 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylated and glycidyl methacrylate copolymer brushes, Chemistry-an Asian Journal, 2014. DOI: 10.1002/asia.201402150, IF: 4.572.
|