News
| Modulating the Structure and Properties of PSS/PDADMAC Multilayers with Concentrated Salt Solutions |
| Time:2012-02-15 15:34 Source:未知 Author:polymer Click: |
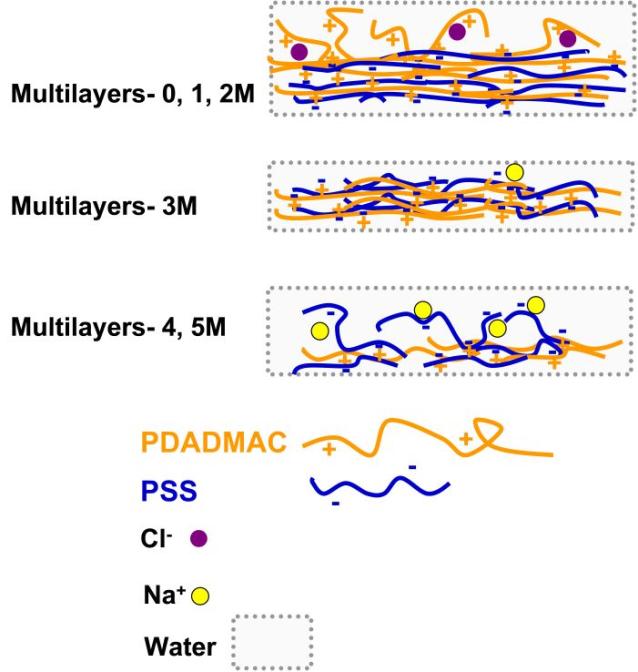
The salt treatment can easily change the structure and physiochemical properties of the PSS/PDADMACmultilayers, resulting in thinfilms with various features. Because the polyanion/polycation stoichiometry in bulk multilayers is observed to be 1:1 or at least close to this value, multilayer 3 M can be regarded as the bulk film because of the roughly equal amounts of PSS and PDADMAC. As a result of the better compensation (5% counterions), the largest cross-linking density is expected among others, leading to the smallest swelling behavior in water. For the thin films with larger numbers of uncompensated for polyions such as multilayers 1 and 5 M, a swollen, hydrated structure is formed. Moreover, because the slight mass loss does not obviously change the multilayer structure, multilayers 0, 1, and 2M can basically maintain their initial physicochemical structure (a PDADMAC-dominated surface). By contrast, the massive loss of polyelectrolytes completely destroys the layered structure of multilayers 4 and 5 M, leading to a surface chemistry reversal. In such a case, the structure is not composed of multilayers any longer. The obtained polymer thin films with various structures and properties are expected to find diverse applications in the fields of biomaterials, medicine, and nanotechnology.
Reference:Lulu Han, Zhengwei Mao, He Wuliyasu, Jindan Wu, Xiao Gong, Yuguang Yang, and Changyou Gao*, Modulating the Structure and Properties of Poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate)/Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) Multilayers with Concentrated Salt Solutions. Langmuir, 2012, 28: 193-199. Download PDF
|